Want to explore more stories and insights from our team?
Do older managers go the extra mile at work?
A new study by Kyriaki Fousiani, Susanne Scheibe, Yannick Griep, and Elissa el Khawli shows that age and managerial status interact in predicting how likely people are to engage in organizational citizenship behavior (OCB). The findings reveal that older managers (rather than younger managers or older non-managers) are more likely to show OCB because they see power as a responsibility. Moreover, older managers are more likely to consider OCB part of their role. Gender also played a role, but less consistently: while older male managers reported the highest OCB in one study, this pattern did not hold in the second study. The results highlight how age and status interactively shape organizational behavior and suggest ways organizations might support OCB among specific employee groups.
Giving & Receiving Feedback Effectively
People react differently to negative feedback—some aim to feel better, while others focus on improving performance. A new study by Felix Grundmann, Kai Epstude and Susanne Scheibe shows that those with a strong performance goal tend to manage their feelings in negative feedback situations by engaging with feedback (e.g., using strategies such as reappraisal), while others may disengage (e.g., using distraction). Goals in feedback situations, in turn, are shaped by how legitimate the feedback appears, the level of negative emotion, and how much attention people pay to their emotions.
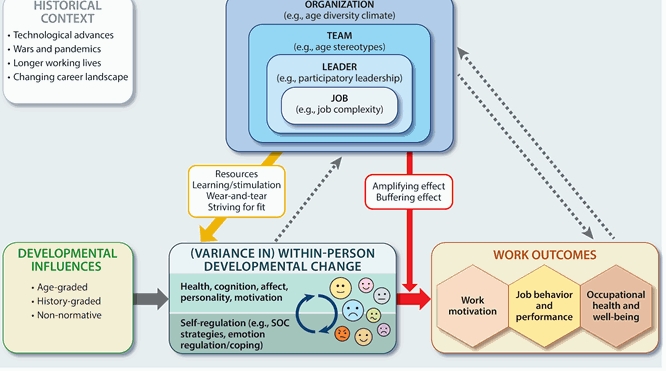
Emotional job demands and the evolution of sympathy in the workplace
Many professions require employees to invest significant emotional effort to succeed. But how does this affect their own emotional growth over time? A recent study by Susanne Scheibe, together with former postdoc researcher Susan Reh (now University of Exeter) delves into this question, exploring how emotional job demands shape employees' sympathy over a 9-year period. They found that working in highly emotionally demanding jobs (such as healthcare or police) can reduce the growth of sympathy over time, leading to less concern and warmth towards others. However, employees with a strong learning goal orientation—those motivated by self-improvement and mastery—are better equipped to buffer these negative effects.
Taming the Narcissistic Leader: How Workplace Culture Shapes Trust
Narcissistic leaders often prioritize their own interests over their followers and organizations, but their behavior can be shaped by workplace culture. This study examines how different workplace environments—performance-focused versus mastery-focused climates—affect the relationship between leader narcissism and employee trust. In performance-driven workplaces, where competition is encouraged, narcissistic leaders are more likely to act selfishly, reducing trust from employees. However, in mastery-focused environments that emphasize collaboration and learning, narcissistic leaders are less likely to engage in self-serving behavior, preserving trust. The research, based on a survey of 546 leaders and 1,718 followers, highlights how workplace culture can either amplify or suppress the negative effects of narcissistic personalities of leaders. Organizations can minimize trust issues by fostering cooperative and ethical environments, ensuring that leadership traits, even negative ones, do not harm employee morale and performance. This study provides valuable insights for businesses aiming to create healthier workplace cultures.
A systematic review of creativity evaluation and creativity selection measurement tasks
Together with Matthijs Baas and Simone Ritter, Eric Rietzschel published a systematic review on research methods in the area of creative idea evaluation and selection. It’s not always easy to recognize and select the most creative option. One of their main conclusions is that the field needs more consistency and methodological integration.
Aleatory creativity
Eric Rietzschel and Diana Rus wrote a chapter on ‘aleatory creativity’ for the recently published book "Constraints in Creativity” (edited by Catrinel Haught-Tromp, Robert Sternberg, and Don Ambrose). Eric and Diana argue that the use of random input for creative purposes has a long history, but has been largely overlooked as a research topic.
Leaders' power construal influences malevolent creativity: The mediating role of organizational conspiracy beliefs
In this study, published in the Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology, Kyriaki Fousiani, Sylvia Xu, and Jan-Willem Van Prooijen explored how employees' perceptions of leaders' power construal—whether seen as responsibility or opportunity—influence employee malevolent creativity through organizational conspiracy beliefs. They found that when a leader's power is predominantly viewed as opportunity it is positively related to organizational conspiracy beliefs among employees. Conversely, when a leader's power is predominantly viewed as responsibility it is negatively related to such beliefs. Organizational conspiracy beliefs in turn, predict employee malevolent creativity targeted at the organization.
Unpacking the relationship between leaders' age and active conflict management: The moderating role of generativity
This research investigates why and when leaders’ age influences their active conflict management strategies. Across two studies, we found that generativity beliefs shape the consequences of leaders' age for their conflict management. More specifically, in Study 1 we found that older leaders with low generativity perceived weaker leader-employee relationship quality (LMX), which negatively influenced their problem-solving and compromising strategies in conflicts with employees. In Study 2, we found that older leaders with high generativity demonstrated stronger emotion regulation knowledge, which was negatively related to their tendency to use forcing strategies in conflicts with employees.
Over depression and burnout
How can we recognize burnout or depression (in employees)? Why do younger employees have burnout symptoms more often than older employees? Susanne Scheibe, together with Marie-José van Tol (Professor of Cognitive Neuropsychiatry at the UMCG) and Annemiek Lely (expert by experience) discussed these and other important questions about depression and burnout at our faculty's Publieksacademie Sociale Wetenschappen in October 2024 at the Forum Groningen.
Empowering women for creative solutions in interpersonal conflict at work
Creativity is essential in managing interpersonal conflict within organizations, yet its drivers remain underexplored. Fousiani, Michelakis, and De Jonge investigated power and gender as key determinants of creativity in interpersonal conflicts at work. Their first study surveyed 226 employees across various organizations, while the second used a conflict simulation with 160 participants in dyads. Both studies examined the impact of relative power (having more power than the other person) on creativity, focusing on how gender influences this relationship. The results revealed a positive link between relative power and creativity in conflict, with a stronger effect among women. Study 2 delved deeper, exploring the distinct dimensions of creativity, such as idea originality and effectiveness. This research provides fresh insights into creativity within organizational conflicts, highlighting the complex interplay of power, gender, and creativity. The findings offer practical implications for organizational leaders and conflict resolution practitioners, emphasizing the critical role of gender dynamics in effective conflict resolution strategies.
Self-care practices and relationships with vitality and health complaints in self-employed workers
This study with 290 self-employed workers shows that individuals‘ engagement in self-care practices positively relates to their well-being. We explored various types of self-care practices and found that physical activities showed the strongest correlation with well-being outcomes. Drawing on the theory of planned behavior, the results further revealed that strong intentions towards practicing self-care positively predicted subsequent self-care practice engagement, even when self-employed workers were faced with entrepreneurial stressors as potential barriers.
Financial Worries, Health Complaints, and Career Exploration: The Role of Action Crises
This study investigates associations between financial worries, a distressing emotional state prompted by perceived threats to financial resources, and employees’ health and career behaviors. We proposed that financial worries are not only positively related to health complaints, but also positively related to employees’ career exploration. We further explored how financial worries are associated with action crises—internal conflicts about whether to leave one’s job—and how these crises may help explain the relationship between worries and employee outcomes. In a two-month time-lagged study with 321 employees, we observed a positive association between financial worries and health complaints, but no significant association with career exploration. Furthermore, the experience of an action crisis mediated the relationship between financial worries and health complaints. Action crises were positively related to subsequent career exploration, and we established a significant indirect effect of financial worries on career exploration through action crises. This research contributes to a better understanding of the potential health-related and career behavioral outcomes of financial worries by introducing action crisis as a cognitive–emotional mechanism.
New publication on boundary management during telework
What can we learn from older workers about teleworking successfully? A new publication by our team points at five specific tactics that older workers tend to use more than younger workers, with benefits for their work-life balance and productivity during telework. These are (1) setting physical boundaries (e.g. working in a dedicated space at home rather than on the kitchen table), (2) setting digital boundaries (e.g. switching off work-related social media after work time), (2) communicating rules with private contacts (e.g. making agreements when it is ok for kids to interrupt during work time), (4) communicating rules with coworkers (e.g. letting coworkers know when one starts and finishes work so they don't disturb during off-work time), and (5) temporal tactics (setting start and end time for working hours into the personal agenda). Organizations may train (especially younger) workers on these tactics, or encourage intergenerational knowledge sharing on these tactics, in order to maximize the benefits of telework, while minimizing its costs.
Faking emotions can help bad bosses get ahead
People with psychopathic tendencies have impaired empathy and remorse, lie and manipulate, and have bold, egotistical traits. Yet they can sometimes successfully climb the ladder to leadership positions. One reason for this might be that such leaders can “hide behind a mask of sanity,” skillfully managing how they express emotions to shape others’ perceptions positively. In our study, involving 306 teams, we explored how leaders' primary psychopathy and their emotion regulation strategies influence followers’ views of the leader's authenticity and trustworthiness. We discovered that leaders with strong psychopathic traits benefit more from surface acting—feigning emotions rather than truly feeling them—to build follower trust. We also found that for leaders with higher levels of primary psychopathy deep acting - truly experiencing the emotions they display- is a less fruitful strategy because they lack the necessary empathic concern. Displaying naturally felt emotions is also positively linked to follower trust. Overall, our findings suggest that leaders with psychopathic characteristics can manipulate how subordinates perceive them through strategic emotional displays. By carefully controlling their emotional expressions via surface acting, these leaders can exploit their followers’ perceptions to maintain power and control.
Financial stress and quit intention: the mediating role of entrepreneurs’ affective commitment
Kleine, Schmitt, and Wisse conducted three studies to examine the association between financial stress in entrepreneurs, their intention to quit their businesses., and the role of entrepreneurs‘ affective commitment —the emotional bonds that they formed with their jobs and businesses—as an underlying factor explaining the association between financial stress and quit intentions. The research highlights the crucial role of financial stress as a hindrance stressor in entrepreneurs.
A Job Demands–Resources Perspective on Emotional Exhaustion and Work Engagement in Human–Animal Work
In a study based on 205 employees who engage in human–animal work, we investigated employees’ perceived job demands and resources that are characteristic of human–animal work and relationships with well-being and motivational outcomes. The results revealed that the job demand of animal distress increased employees' emotional exhaustion, while the demand of occupational stigma was not significantly related to exhaustion. The job resources pro-animal impact and human-animal bonds positively predicted employees’ work engagement. However, when employees reported that the animals they were working with experienced distress, the association between human-animal bonds and work engagement was mitigated. We discuss implications for the job demands–resources theory, research on animal distress, and the field of human–animal work, and offer practical implications for employees working with animals.
Competitive organizational climate and artificial intelligence (AI) acceptance: the moderating role of leaders’ power construal
Artificial intelligence (AI) stands at the forefront of the fourth industrial revolution, where organizations are strategically integrating it as a vital tool to address a diverse range of daily management and work-related challenges. Yet, despite the advantages of AI, employees frequently perceive AI as a double-edged sword with unintended consequences. Kyriaki Fousiani and colleagues investigated how work climate influences employee attitudes toward AI and actual AI use. They found that a competitive climate increases AI acceptance over time (i.e., positive attitude and use), but only when leaders use their power as a responsibility to serve their team rather than as an opportunity to promote their agenda. The results of this study underscore the organizational factors that are required in order for employees to shape favorable attitudes towards AI and actually use AI at work.
Animal roles in organizations: A framework for exploring organizational human–animal relations
Despite the growing body of research on human–animal studies in various disciplines, attempts to systematically include animals in organization studies have been limited. In this article, Kandel, Dlouhy, and Schmitt build on organizational role theory and propose a typology of five roles of animals in human organizations (i.e., animals as commodities, clients, co-workers, companions, and acquaintances) as a framework for analyzing organizational human–animal relations.